Update 1: Alderpersons Quinn and Mitchell “deferred and published” the ADU ordinance on Wednesday, July 16, 2025, which means it was not voted on and must be taken up again at a future City Council meeting.
Update 2: Help get the ordinance over the finish line on September 25, 2025. I made a list of events and actions and everyone can contribute something.
The Chicago City Council zoning committee voted to approve citywide accessory dwelling units (ADUs). I was sick this morning and late to the meeting so I couldn’t sign up for the public comment roster. My planned comment is at the end of this post.
The most substantial change from the last proposal (circa May 2024) is that ADUs will be allowed in residential buildings in all zoning districts subject to the following caps:
- RS-1: one ADU permit per block (both sides of the street) per year
- RS-2: two…
- R3-3: three…
- Other zoning districts: no cap
There is also an owner occupancy requirement, to be proved at the time of permit application, to build an ADU in the RS zoning districts. The version text that passed is not yet available online, but it will be posted under ordinance SO2024-0008918.
Read WTTW’s report on what alderpersons said about ADUs, including the despicable comments about migrants by one of them.
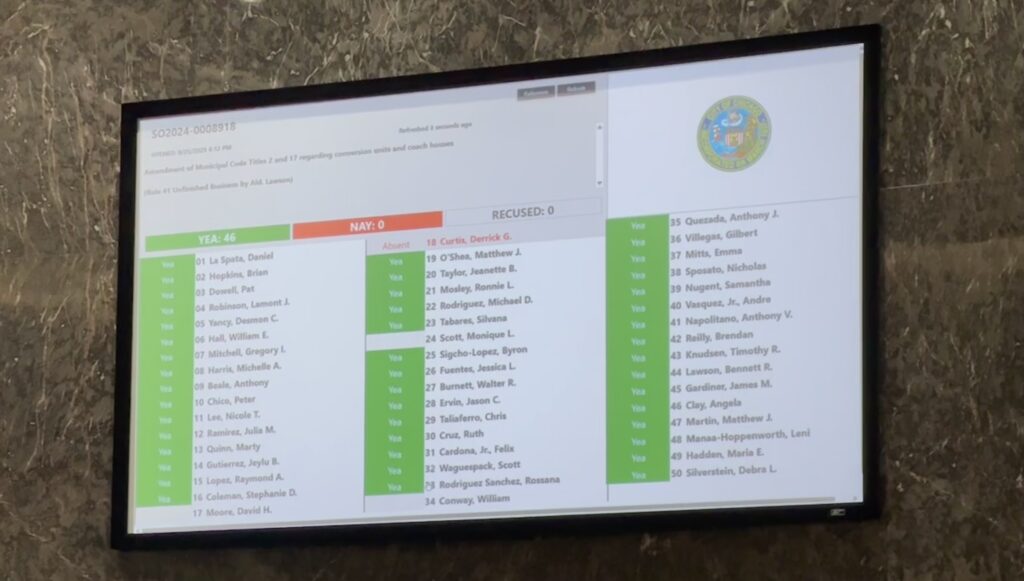
The full City Council will vote on this ordinance tomorrow; I think it will pass by one or two votes. The lists below shows how committee members voted, approving it 13 to 7 (with all zoning committee members present).
Yes on ADUs:
- La Spata
- Hall
- Ramirez
- Sigcho-Lopez
- Fuentes
- Burnett
- Cruz
- Conway
- Quezada
- Villegas
- Knudsen
- Clay
- Lawson
No on ADUs:
- Hopkins
- Dowell
- Harris
- Beale
- Moore
- Mosley
- Reilly
Public comment
Hi my name is Steven Vance. I live in the 34th Ward and I’m a volunteer member of Abundant Housing Illinois. Today is a test for the Committee on Zoning. Alderperson Lawson and Mayor Johnson have presented a new version of allowing accessory dwelling units, including coach houses and other types of ADUs, for your favorable vote. The test is whether this body will recognize the mounting evidence of a housing crisis in Chicago and adopt ordinances that will more quickly chip away at the housing shortage.
The most glaring problem, measured by national researchers, is that Chicago’s rents are climbing faster than in any of the other top 50 metropolitan areas, and for sale inventory is so low that houses sell in days at prices tens of thousands of dollars over asking. “Sounds good” for the individual owners and sellers, respectively, but it’s bad for everyone else.
The city’s housing department staff know what is known nationally: that ADUs are one of the most sensible and impactful ways to increase housing options and reduce rents. With the ADU ordinance before you today Chicago would join Los Angeles, New York City, Boston, and Austin, cities where ADUs have been legal since before the pilot began.
To those alders who sometimes or often disagree with Mayor Johnson’s agenda, consider that allowing ADUs across Chicago was first proposed by Mayor Emanuel in his administration’s final five-year housing plan back in 2019, and that it was during Mayor Lightfoot’s administration that the council started the three-year pilot program.
To those who worry that ADUs bring in more children to the neighborhood who might crowd schools, consider that across the city enrollment in public schools is declining and more families and children staying in the city would be a blessing. Mayor Johnson’s amendment considered this by capping the number of ADUs that can be built on each block.
I’m given two minutes so I can’t address every concern, but this committee has had plenty of time to address the concern of Chicagoans: the Chicagoans whose rents are rising too fast for them to afford, and who are having to move every year in search of a cheaper place away from their friends, family, and jobs. The ADU pilot program has brought 100s of new homes online in the last four years without any subsidy from the city. More ADUs means more homes for families to care for someone else: a grandparent staying nearby to care for a newborn, an adult child starting a new family near their parents, and seniors who would age in place by downsizing into a smaller home on their own property or down the street. Vote yes and pass the test.